Community WiFi
Community Cluster is based on the Community WiFi concepts, it simply expands its scope to including collaborating on many other resources, not just networking.
1. Existing Community WiFi
There are many Community Networks around the world, for example in Germany, Greece, Spain, USA , Austria, South Africa etc.
It is interesting that similar community wireless efforts which will be most useful in less developed countries (e.g in Nepal) has stopped while they are still going in more advanced countries (e.g. from wifi hobbyists in Australia to farmers in Italy to low income families in USA).
Area Mesh pushes high tech collaboration between citizens to the limit, from reporting pot holes on the road to helping elderly do shopping.
2. Existing Mobile Carriers
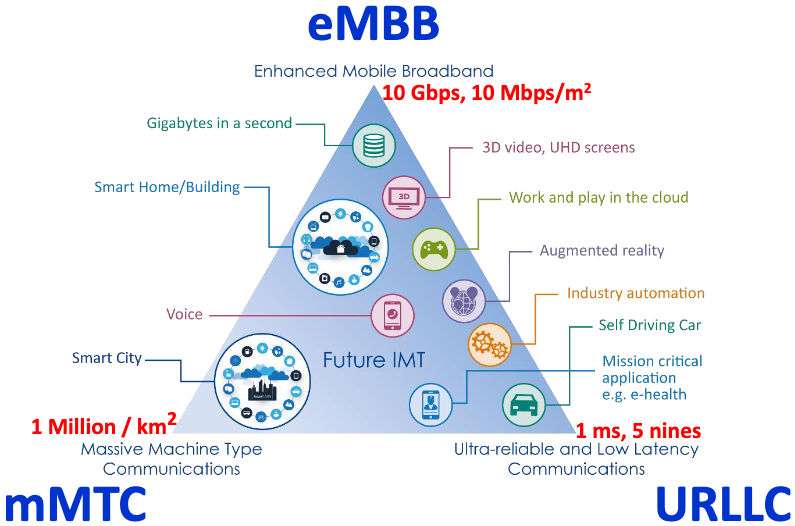
Most mobile carriers are migrating to 5G in order to to gain improved capacity (eMBB), latency (URLLC), density (mMTC).
source: dspcsp
One important feature of 5G not commonly list (e.g. missing above) is it positioning ability, which was first introduced in 5G release 15 in 2017 (target accuracy 50m) with increasing accuracy and capability in every following release (the latest 5G release 18 in 2024 has target accuracy of less than 0.5m). Deployment of 5G positioning in the field is still very limited due to reliability, cost, power consumption etc.
5G's carrier centric approach relies on carrier built infrastructure (e.g. mobile towers, fibre backhaul etc.) and carrier defined services (e.g. URLLC, eMBB etc.).
Area Mesh complements those same 3 service areas
Scaling Up Community Networks
Community Cluster provides communities large or small with their OWN physical and virtual networks.
Using the revolutionary Team Compute paradigm , Community Cluster removes the skill and cost barriers to the building and operating of Community Networks by dividing the network up into fixed size cells.
Area Mesh enables you to turn those annoying wifi signals from your neighbours into an indoor geo-positioning system or use those wifi as backup links when you own internet link is down.
Besides enabling communities to create of millions of application and community specific Virtual Clusters (at the IP level), Community Cluster Compute Assets.
1. Roof Stations
A secure and private communication network is required to underpin collaboration between citizens.
The MIT Roofnet is an early example of a roof based network where radios on the roofs in the neighbourhood talk to each other, forming an independent high speed data network.
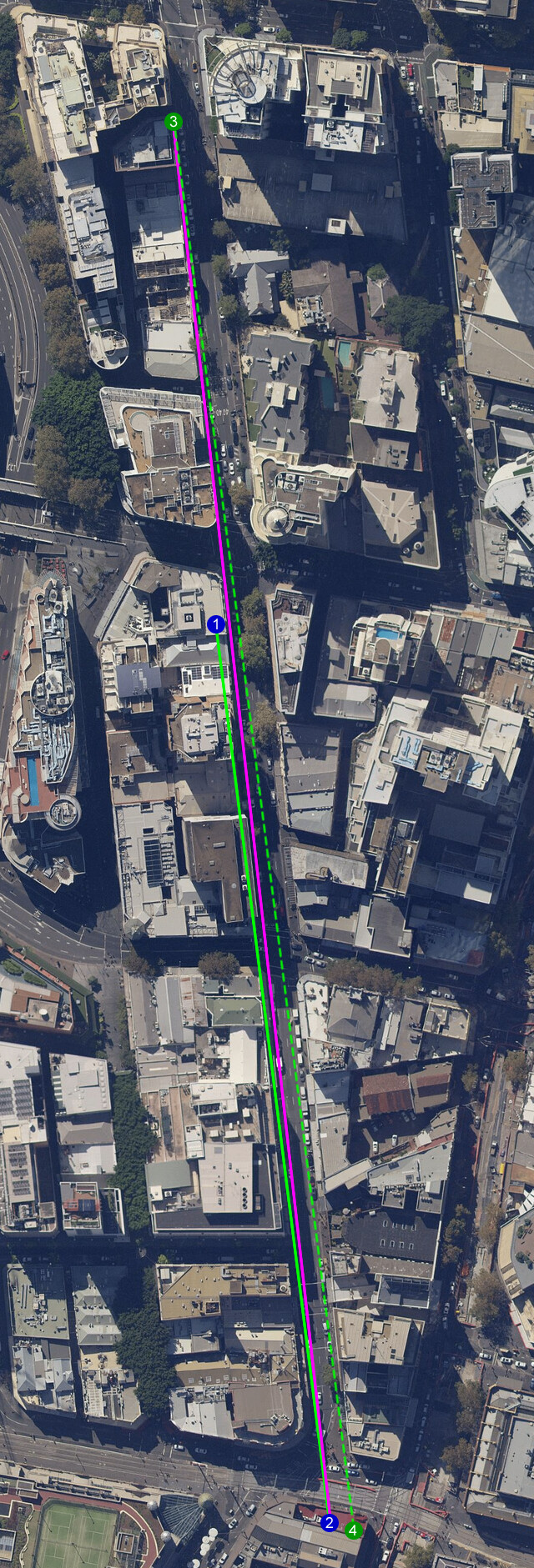
A radio mesh on the roof is cool since we can also interact with Unmanned Autonomous Vehicles (UAVs) easily on the roof e.g. refuelling them like in Float Mesh nodes. However, the installation of equipment, line of sight requirement etc. make it very difficult to achieve wide adoption. We started on the roofs of some buildings in Sydney using Australian WiFi Frequencies and Australia LoRa Frequencies.
About a year after we have linked 3 buildings (points 1, 2, 3 in above image) together with roof top radios, a new hotel was built in the middle blocking the WiFi signals between point 2 and 3. We now have to install another radio at point 4 in order to maintain roof top connection between all 3 buildings (this installation might be part of the planned 2022 year end meet up in Sydney).
As can be seen, roof node s can be challenging to deploy and operate.
For cities that have 4G in the air and fibre in the ground, we have put the deploying roof top radios on hold. We are still using radio mesh in other cases e.g. Float Mesh and Water Pile, but Virtual Private Mesh over the Internet, which can be deployed with just one command, is now the preferred method linking citizen sites within cities together.
2. Window Stations
With increasing restrictions on UAVs in the city, the advantages of placing Nearby Mesh Nodes on the roof have reduced. And as can be seen in our Roof Top deployment above, building up such a network can be difficult.
However, placing indoor nodes near a window and outdoor nodes on a balcony can still be viable, we will need to investigate that next.